1 Installing and setting up tools
Following are the steps to installing R, RStudio, and Git depending on your operating system.
1.1 Installing R, RStudio, and git
Step 1: Download and install R
Important that R is installed first. R is the main software and is needed for RStudio to work properly. R should always be installed first.
Go to https://cran.r-project.org and click on the link that says Download R for Windows. In the following page, click on the link that says install R for the first time.
Then click on Download R-4.X.X for Windows (latest release version). This will start the download process.
Once downloaded, go to the .exe file in your Downloads folder, double-click and follow all the install prompts, selecting recommended options all the time.
Step 2: Download and install RStudio
This step requires that Step 1 has been done and was successful.
Go to https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/ and select the download specific for your Windows machine.
Once downloaded, double-click on .exe file downloaded to your Downloads folder and then follow all install prompts, always selecting recommended options.
Step 3: Download and install Rtools
For the things that you will be taught in the Open and Reproducible Science sub-module, you we will need to expand the installation of R by installing the Rtools software.
Go to https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/Rtools/ and choose to download the latest version of the installer (which is the Rtools version compatible with the R version you have installed in Step 1).
Once you have downloaded the .exe file, double-click on the .exe file and follow all install prompts. Choose all the recommended options.
Step 4: Download and install Git for Windows
For the things that you will be taught in the Open and Reproducible Science sub-module, you we will need to install Git for Windows.
Go to this link - https://github.com/git-for-windows/git/releases/latest - to download the latest version of git. Make sure to select the version compatible with your Windows machine (64-bit or 32-bit).
Once you have downloaded the .exe file, double-click it and then follow all install prompts. Choose all recommended options.
Step 1: Download and install R
Important that R is installed first. R is the main software and is needed for RStudio to work properly. R should always be installed first.
Go to https://cran.r-project.org and click on the link that says Download R for macOS. In the following page, you will have two choices of R versions to install. Make sure to install the appropriate version for your macOS version (Apple Silicon vs Apple Intel version). Click on the download link for your macOS version. This will start the download process of the .pkg file specific for installing in macOS computers.
Once downloaded, go to the .pkg file in your Downloads folder, double-click and follow all the install prompts, selecting recommended options all the time.
1.1.1 Install RStudio
This step requires that Step 1 has been done and was successful.
Go to https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/ and select the download specific for your macOS machine.
Once downloaded, double-click on .dmg file downloaded to your Downloads folder and then follow all install prompts, always selecting recommended options.
1.1.2 Install git for macOS
For the things that you will be taught in the Open and Reproducible Science sub-module, you we will need to install git for macOS. Apple machines are already pre-installed with git but it is usually an Apple specific version of git and tends to be older and not configured in the way we need it. So we need to install another version of it that comes with Apple’s Xcode command line tools.
To install, go to the macOS terminal and type the following command:
xcode-select --install1.2 Register a GitHub account
For the Open and Reproducible Science in R sub-module, you will need a GitHub account to be able to receive the code materials and assignments that will be provided. This is the mechanism by which these materials will be distributed. Hence you will need to register an account with GitHub (if you don’t already have one). It’s free!
Step 1. Sign-up to GitHub
Go to https://github.com.
On the upper right hand corner of the page, click on Sign-up button
You will be then prompted to provide an email address to register your account with.
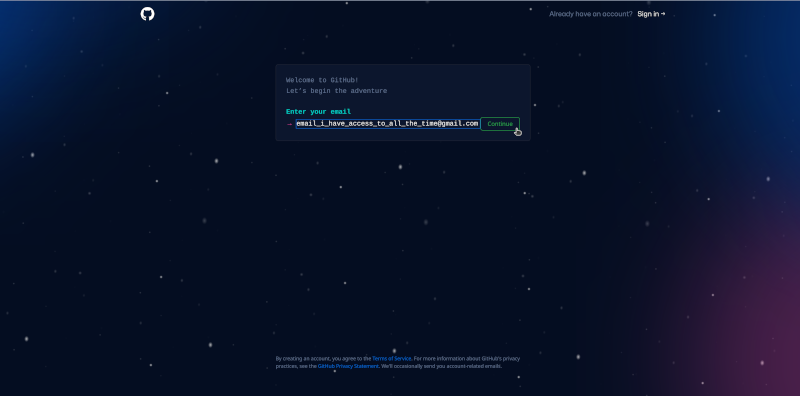
With regard to the email address to use for creating a GitHub account, best practice is to use an email address that you will have access to all the time. Email addresses such as those for school (if you are a student) or for your current work may not always be the best email address to use as these email addresses tend to be time-limited (i.e., you lose the email address once you graduate or once you leave your current work).
You will then be prompted for a password

Then follow all other prompts after this including confirmation of your email and creating a GitHub username (see next step).
Step 2. Set a GitHub username
With regard to creating/selecting a GitHub username, following are some best practice recommendations (Jenny Bryan and Jim Hester n.d.).
Incorporate your actual name as this lets people know who they’re dealing with and also makes your username easier for people to guess or remember.
Reuse your username from other contexts, e.g., Twitter or Slack.
Pick a username that will be appropriate revealing to a future boss.
Shorter is better than longer.
Be as unique as possible in as few characters as possible.
Make it timeless and context-agnostic. Don’t add a date or year or a reference to your current location, university, or employer.
Avoid the use of upper vs. lower case to separate words. We highly recommend all lowercase. A better strategy for word separation is to use a hyphen (-).
Step 3. Setup two-factor authentication (2FA)
It is important to keep your GitHub account secure. Any breach in security of your online accounts, including GitHub, not only affects you but also those that you collaborate with. To increase the security of your GitHub account, please enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your account. This can be done here. There are 4 options for 2FA in GitHub. We recommended enabling at least 2 of these options. If you are familiar with use of passkeys, we recommend using this authentication approach in addition to 2FA.
Step 4. Get added to the Oxford IHTM GitHub organisation
The Oxford iHealth GitHub organisation is the organisational GitHub account for the MSc IHTM. To be included in the organisation, share your GitHub username to the sub-module lead who will then add you to the organisation. This is an important step as assignments and exercises for the sub-module are distributed through GitHub and GitHub Classroom via this organisational account.
The Oxford iHealth organisational GitHub account requires members to have 2FA activated. It is therefore imperative that you enable 2FA on your account to be included in the organisation.
You will soon receive a message at the email address you registered to GitHub with inviting you to join the Oxford iHealth organisation. Accept the invitation.